
The fluid makes the hair cells move, too. The vibrations make the fluid in the inner ear move.
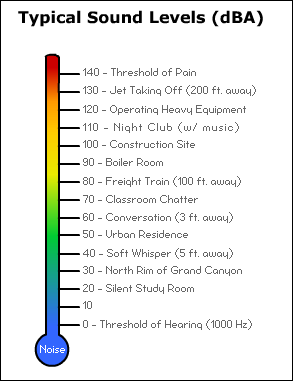
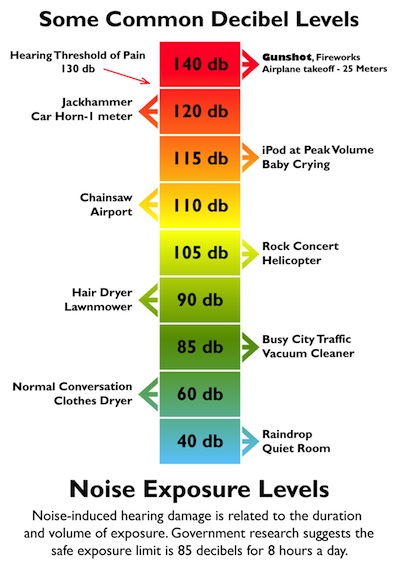
The cochlea is filled with fluid and has tiny hair cells along the inside. The last of the three middle ear bones moves the sound vibrations into the inner ear, or cochlea.The movement makes the sound vibrations bigger. The sound vibration makes the three middle ear bones move.The sound wave travels down the ear canal toward your eardrum. The outer ear, which is what you see on the side of your head, collects the sound wave.The louder the sound, the bigger the sound wave. Sound goes into your ear as sound waves.How do loud noises hurt your hearing? It may help to first understand how you hear: It can last for a few minutes or a few days. You have pain or ringing in your ears after you hear the noise, called tinnitus.Speech around you sounds muffled or dull after you leave the noisy area.You can't hear or understand someone 3 feet away from you.So how can you know if noises are too loud? Here are some signs: You probably don't always carry a sound level meter with you. The noise chart was developed using the following two websites: Moderate-Safe listening for any time periodħ0 dBA = group conversation, vacuum cleaner, alarm clockĦ0 dBA = typical conversation, dishwasher, clothes dryer Very loud-Dangerous to hearing wear earplugs or earmuffsĩ1 dBA = subway, passing motorcycle, gas mower Painful steady noise-Not safe for any period of timeġ20 dBA = jet plane takeoff, siren, pneumatic drillĮxtremely loud-Dangerous to hearing wear earplugs or earmuffsġ12 dBA = maximum output of some MP3 players, rock concert, chainsawġ00 dBA = tractor, listening with earphonesĩ4 dBA = hair dryer, kitchen blender, food processor Painful impulse noise-Not safe for any period of timeġ50 dBP = fireworks at 3 feet, firecracker, shotgun The noise chart below lists average decibel levels for everyday sounds around you. Impulse noise greater than 140 dBP will hurt your hearing right away. We measure impulse noise in dB peak pressure, or dBP. This noise, called impulse noise or impact noise, may come from gunfire or fireworks. Ī single loud blast or explosion that lasts for less than 1 second can cause permanent hearing loss right away.

Information on levels of environmental noise requisite to protect public health and welfare with an adequate margin of safety Retrieved from. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Noise Abatement and Control. World Health Organization, WHO-ITU global standard for safe listening devices and systems, 2019.The recommendations would also have safe listening information appear on external product packaging and advertising, as well as on manufacturers' websites. The World Health Organization and International Telecommunication Union 2019 document, WHO-ITU Global Standard on Safe Listening Devices and Systems , recommends that manufacturers equip devices like smartphones and personal audio players with information that explains safe listening (for adults, a total of 40 hours of weekly exposure to volume levels no higher than 80 dB is recommended for children, the level is 75 dB) usage warnings and tracking information cues for taking safe listening actions options for limiting volume levels and volume limiters expressly for parents to use. And if the sound goes up to 91 dBA, your safe listening time is down to 2 hours. If the sound goes up to 88 dBA, it is safe to listen to those same sounds for 4 hours. For example, you can listen to sounds at 85 dBA for up to 8 hours. The safe listening time is cut in half for every 3-dB rise in noise levels over 85 dBA. Sounds over 85 dBa can damage your hearing faster. Sounds at 85 dBA can lead to hearing loss if you listen to them for more than 8 hours at a time. You can listen to sounds at 70 dBA or lower for as long as you want. The higher the noise level, the louder the noise. We record noise levels in decibels, or dBA. These sounds can last a long time, like listening to a concert, or they can be short, like from gunfire. Noise-Induced Hearing Loss, or NIHL, happens when you listen to loud sounds. Loud noise can cause permanent hearing loss.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
